With Impressionism – Expressionism: Art at a Turning Point, the Nationalgalerie, Staatliche Museen zu Berlin presents a groundbreaking exhibition at the Alte Nationalgalerie from 22 May to 20 September 2015, deliberately comparing these two artistic styles for the first time.
The Nationalgalerie was one of the first museums in the world to acquire Impressionist paintings, beginning in 1896; by 1919, the museum had added an extensive collection of Expressionist works. The comprehensive exhibition at the Alte Nationalgalerie will trace the similarities and differences between these two art movements, a process of comparison that began just after 1900. Over 160 Impressionist and Expressionist masterpieces from chiefly German and French artists will be on display, assembled from the collections of the Nationalgalerie and other museums around the world.
The development of Impressionism is associated with artists such as Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, Camille Pissarro, and Pierre-Auguste Renoir in France and with painters including Max Liebermann, Lovis Corinth, and Max Slevogt in Germany. Works by Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, Erich Heckel, Karl Schmitt-Rottluff, Emil Nolde, and Franz Marc epitomize the powerful counter-movement of Expressionism in Germany.
Occupying the entire middle floor of the Alte Nationalgalerie, the exhibition is arranged according the principle shared motifs of the two movements. The main hall is devoted to the theme of the city; further rooms treat night life in bars, cafes, and restaurants, leisure time spent at the outskirts of the city, as well as themes of family, artists, and art mediators. The motif of the bather opens the exhibition and stands in sharp contrast to the final room with works from 1913 which capture the simmering sense of unease at that time.
A comprehensive catalogue published by Hirmer Verlag accompanies the exhibition, containing numerous essays and 230 full-colour illustrations.
No two other styles were as intensely and unsparingly contrasted with one another in their time as
Impressionism and Expressionism. Impressionism is inextricably linked with France and with artists
such as Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, and Auguste Renoir. The German Impressionism of Max
Liebermann, Lovis Corinth, and Max Slevogt developed in the 1890s as a response to the movement
in France. A fierce backlash followed shortly thereafter with the advent of Expressionism, spearheaded
by painters such as Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, Erich Heckel, Emil Nolde, and Franz Marc in Germany.
The simultaneous emergence of these two styles provided critics and theorists with an ideal basis to
compare the seemingly antithetical cultures of France and Germany. It was gallery owner Herwarth
Walden who first spoke of a ‘turning point’ in the transition from Im(pressionism) to Ex(pressionism).
Despite the stark distinction that would later be drawn between the two styles, Impressionism and early Expressionism share surprisingly many characteristics. Both movements take an anti-academic stance, hold painting en plein air in high regard, portray immediate experiences of light and colour, and focus on the material details of the artists’ surroundings. In addition, subjectivity and the individual character of each artist’s brushwork were highly prized among exponents of both artistic movements.
The Nationalgalerie is closely tied to the history of artists working in both styles. Through its director, Hugo von Tschudi, the Nationalgalerie was the first museum in the world to acquire Impressionist paintings, beginning in 1896 even before the Paris museums. Tschudi’s successor, Ludwig Justi, on the other hand, amassed a spectacular collection of Expressionist works after 1918 for the new wing of the Nationalgalerie, at the former crown prince’s palace on Unter den Linden. Moreover, Justi developed a ‘School of Seeing’ over many years, which aimed to elucidate the particular characteristics of various artworks by comparing them to one another.
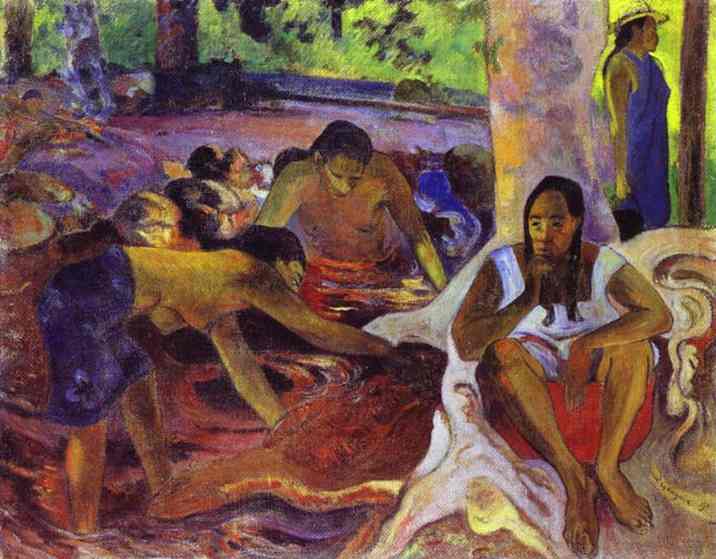
Bathers
Variations on the theme of the bather in pastoral and idyllic settings have been found since antiquity. Bathing figures became a major motif in the paintings of late Impressionism and Expressionism as well. Paul Cézanne's images of unclothed men or women by the water, were not painted from nature but were carefully conceived and staged in his studio. They became the much-admired ideal for artists from both movements. The naked bodies which no longer met ideals of beauty, the absence of a mythological overlay and the reduction of shapes and spatial relationships all had a provocative effect. They inspired Cézanne’s contemporaries Pissarro, Degas, and Renoir from the end of the nineteenth century, and later influenced German artists such as Liebermann, Kirchner, and Pechstein.
The modernist representations of bathers outdoors in nature, at the Moritzburg lakes and on the beaches of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea were based on a dream of a benevolent togetherness, close to nature and far from the stifling rules of the bourgeois world. Other painters looked for true ‘primitiveness’ in the South Seas, among the natives of Tahiti or Papua New Guinea. At the same time, however, the artists’ representations of people bathing, resting, or drying themselves also celebrate the pure joy of living and the appeal of nudity.

Out of Doors
The idea and experience of leisure time developed in the nineteenth century as a result of urbanization and industrialization, which entailed a life with fixed working hours. Leisure was seen as the private part of one’s life, and was regarded as a counterweight to the all-consuming world of work. Peace and quiet, amusing diversions and stimulating time spent together with friends and family offered a change of scene and the chance to relax. Recently constructed railways allowed members of the working class and middle class to travel to the city’s outskirts and into the countryside, away from the noise and stench of the metropolis.
The Impressionists and Expressionists also heeded the call of the countryside and sought to redefine their relationship with nature within the context of recreational spaces. Here, even more than in the city, they employed the technique of painting en plein air using tubes of paint invented around 1840, which dried up less quickly and were easy to transport. River banks, meadows, and gardens, public parks, zoos, and lively spots in restaurants along the Seine in Paris or the Alster lake in Hamburg served as the artists’ subjects. Impressionism and Expressionism were the last modern and comprehensive styles to provide an unmediated, realistic view of ordinary people’s everyday lives.
The urge to travel to the countryside is as old as the city itself, dating back to antiquity. Representations of villas in the verdant locations can be found in Pliny and Vitruvius, forming the models on which architects and land owners based their country estates as late as the nineteenth century. Most of these homes were surrounded by carefully landscaped gardens and parks and were viewed as places of relaxation and repose. Shielded from the outside world, these estates served as retreats from the hectic bustle of the city, offering their owners not only a chance to connect with nature but also to increase their social standing.
Towards the end of the nineteenth century, the garden became a popular and important motif for the avant-garde due to purely artistic reasons. Representations of gardens were not subject to an established tradition but rather were set in opposition to the generic canons of academic painting. Many artists including Claude Monet, Max Liebermann, Max Slevogt, and Emil Nolde acquired a
Couples and Relationships
Art Mediators. Dandies, Connoisseurs, Patrons, and Collectors
Still Lifes
Behind closed doors
Despite the stark distinction that would later be drawn between the two styles, Impressionism and early Expressionism share surprisingly many characteristics. Both movements take an anti-academic stance, hold painting en plein air in high regard, portray immediate experiences of light and colour, and focus on the material details of the artists’ surroundings. In addition, subjectivity and the individual character of each artist’s brushwork were highly prized among exponents of both artistic movements.
The Nationalgalerie is closely tied to the history of artists working in both styles. Through its director, Hugo von Tschudi, the Nationalgalerie was the first museum in the world to acquire Impressionist paintings, beginning in 1896 even before the Paris museums. Tschudi’s successor, Ludwig Justi, on the other hand, amassed a spectacular collection of Expressionist works after 1918 for the new wing of the Nationalgalerie, at the former crown prince’s palace on Unter den Linden. Moreover, Justi developed a ‘School of Seeing’ over many years, which aimed to elucidate the particular characteristics of various artworks by comparing them to one another.
Bathers
Variations on the theme of the bather in pastoral and idyllic settings have been found since antiquity. Bathing figures became a major motif in the paintings of late Impressionism and Expressionism as well. Paul Cézanne's images of unclothed men or women by the water, were not painted from nature but were carefully conceived and staged in his studio. They became the much-admired ideal for artists from both movements. The naked bodies which no longer met ideals of beauty, the absence of a mythological overlay and the reduction of shapes and spatial relationships all had a provocative effect. They inspired Cézanne’s contemporaries Pissarro, Degas, and Renoir from the end of the nineteenth century, and later influenced German artists such as Liebermann, Kirchner, and Pechstein.
The modernist representations of bathers outdoors in nature, at the Moritzburg lakes and on the beaches of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea were based on a dream of a benevolent togetherness, close to nature and far from the stifling rules of the bourgeois world. Other painters looked for true ‘primitiveness’ in the South Seas, among the natives of Tahiti or Papua New Guinea. At the same time, however, the artists’ representations of people bathing, resting, or drying themselves also celebrate the pure joy of living and the appeal of nudity.
Paul Cézanne
Sieben Badende (Sept baigneurs), um 1900 Seven Bathers, circa 1900 Öl auf Leinwand, 38 x 46 cm Fondation Beyeler, Riehen/Basel, Sammlung Beyeler |
|
Emil Nolde
Papua-Jünglinge, 1914 Papuan Youths, 1914 Öl auf Leinwand, 70 x 103,5 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie |
|
Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Badende mit blondem, offenem Haar (Baigneuse blonde aux cheveux dénoués), um 1903 Bather with Loose Blonde Hair, circa 1903 Öl auf Leinwand, 92,7 x 73,4 cm Wien, Belvedere |
|
City, Suburb, Pedestrians
Impressionism and Expressionism are urban cultures. Artists from both movements discovered the beauty of the growing metropolises for themselves: from the 1860s, Claude Monet and his fellow Impressionists were inspired by Paris, while from 1900, the Expressionists focused mainly on Berlin. Both cities were a source of artistic innovations in their time.
Rapidly changing cities with their increasingly busy streets, glittering lights, broad boulevards, and bustling squares became a key motif for artists. In 1863, Charles Baudelaire described a painter wandering through the city as a flâneur: ‘He is looking for that something which you must permit me to call modernity.’ That ‘something’ also included darting pedestrians and cocottes in the city at night, the new means of transport and electric lights. Cityscapes seen by rain, fog or snow helped artists including Camille Pissarro and Lesser Ury, as well as Max Beckmann and Otto Dix, to make a variety of artistic discoveries. The artists’ subjective sensibilities, which were a product of their respective time, are captured in these images.
The motif of the bridge crops up surprisingly often, including both traditional bridges over rivers and the new railway bridges. Frequently, it is precisely these pictures that testify to a poetic treatment of the cityscape, by means of reflections in the water and the depiction of space in atmospheric tones.
Impressionism and Expressionism are urban cultures. Artists from both movements discovered the beauty of the growing metropolises for themselves: from the 1860s, Claude Monet and his fellow Impressionists were inspired by Paris, while from 1900, the Expressionists focused mainly on Berlin. Both cities were a source of artistic innovations in their time.
Rapidly changing cities with their increasingly busy streets, glittering lights, broad boulevards, and bustling squares became a key motif for artists. In 1863, Charles Baudelaire described a painter wandering through the city as a flâneur: ‘He is looking for that something which you must permit me to call modernity.’ That ‘something’ also included darting pedestrians and cocottes in the city at night, the new means of transport and electric lights. Cityscapes seen by rain, fog or snow helped artists including Camille Pissarro and Lesser Ury, as well as Max Beckmann and Otto Dix, to make a variety of artistic discoveries. The artists’ subjective sensibilities, which were a product of their respective time, are captured in these images.
The motif of the bridge crops up surprisingly often, including both traditional bridges over rivers and the new railway bridges. Frequently, it is precisely these pictures that testify to a poetic treatment of the cityscape, by means of reflections in the water and the depiction of space in atmospheric tones.
Max Beckmann
Straße bei Nacht, 1913 Street at Night, 1913 Öl auf Leinwand, 90 x 70 cm Privatbesitz |

Gustave Caillebotte
Trocknende Wäsche am Ufer der Seine (Linge séchant au bord de la Seine, Petit Gennevilliers), um 1892 Laundry Drying on the Bank of the Seine, circa 1892 Öl auf Leinwand, 105,5 x 150,5 cm Köln, Wallraf-Richartz-Museum & Fondation Corboud, Leihgabe Kuratorium und Förderergesellschaft Wallraf-Richartz- Museum/Museum Ludwig e.V. |
|
Otto Dix
Straßenlaternen, 1913 Street Lamps, 1913 Öl auf Papier auf Spanplatte, 51,3 x 62,9 cm Dauerleihgabe der Otto Dix Stiftung Vaduz in der Kunstsammlung Gera |
|
Ernst Ludwig Kirchner Potsdamer Platz, 1914 Potsdamer Platz, 1914 Öl auf Leinwand, 200 x 150 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie, erworben mit Unterstützung der Kulturstiftung der Länder, der Bundesrepublik Deutschland, der Ernst von Siemens Kunststiftung, der Kultur-Stiftung der Deutschen Bank und anderer |
Ernst Ludwig Kirchner
Der Belle-Alliance-Platz Berlin, 1914 Belle-Alliance-Platz, Berlin, 1914 Tempera auf Leinwand, 96 x 85 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie, erworben durch das Land Berlin |
|
Out of Doors
The idea and experience of leisure time developed in the nineteenth century as a result of urbanization and industrialization, which entailed a life with fixed working hours. Leisure was seen as the private part of one’s life, and was regarded as a counterweight to the all-consuming world of work. Peace and quiet, amusing diversions and stimulating time spent together with friends and family offered a change of scene and the chance to relax. Recently constructed railways allowed members of the working class and middle class to travel to the city’s outskirts and into the countryside, away from the noise and stench of the metropolis.
The Impressionists and Expressionists also heeded the call of the countryside and sought to redefine their relationship with nature within the context of recreational spaces. Here, even more than in the city, they employed the technique of painting en plein air using tubes of paint invented around 1840, which dried up less quickly and were easy to transport. River banks, meadows, and gardens, public parks, zoos, and lively spots in restaurants along the Seine in Paris or the Alster lake in Hamburg served as the artists’ subjects. Impressionism and Expressionism were the last modern and comprehensive styles to provide an unmediated, realistic view of ordinary people’s everyday lives.
Out of Doors. The Creation of Leisure
Marie Bracquemond
Die Teestunde (Le Goûter), 1880 Tea Time, 1880 Öl auf Leinwand, 81,5 x 61,5 cm Petit Palais, Musée des Beaux-Arts de la Ville de Paris |
|
Lovis Corinth Der neue See im Berliner Tiergarten, 1903 Neue See in the Tiergarten, Berlin, 1903 Öl auf Leinwand, 76 x 100,5 cm Kunsthalle Mannheim |
|
Raoul Dufy Hafen (Le Port), 1908 Harbour, 1908 Öl auf Leinwand, 65 x 81 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie |
|
Erich Heckel
Schlafender Pechstein, 1910 Pechstein, Sleeping, 1910 Öl auf Leinwand, 110 x 74 cm Buchheim Museum der Phantasie, Bernried am Starnberger See |
|
Erich Heckel
Kanal im Winter, 1913/14 Canal in Winter, 1913/14 Öl auf Leinwand, 70 x 80 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie |
|
August Macke
Spaziergang in Blumen, 1912 Walk among Flowers, 1912 Öl auf Leinwand, 63,5 x 48,5 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie, erworben durch das Land Berlin |
|
Claude Monet
Die Barke in Giverny (En norvégienne), um 1887 In the Rowing Boat at Giverny, circa 1887 Öl auf Leinwand, 97,5 x 130,5 cm Paris, Musée d’Orsay, Geschenk der Prinzessin Edmond de Polignac, 1947 |
|
Auguste Renoir
Blühender Kastanienbaum (Le Marronnier en fleurs), 1881 Chestnut Tree in Bloom, 1881 Öl auf Leinwand, 71 x 89 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie |
Villas and Country Homes
The urge to travel to the countryside is as old as the city itself, dating back to antiquity. Representations of villas in the verdant locations can be found in Pliny and Vitruvius, forming the models on which architects and land owners based their country estates as late as the nineteenth century. Most of these homes were surrounded by carefully landscaped gardens and parks and were viewed as places of relaxation and repose. Shielded from the outside world, these estates served as retreats from the hectic bustle of the city, offering their owners not only a chance to connect with nature but also to increase their social standing.
Towards the end of the nineteenth century, the garden became a popular and important motif for the avant-garde due to purely artistic reasons. Representations of gardens were not subject to an established tradition but rather were set in opposition to the generic canons of academic painting. Many artists including Claude Monet, Max Liebermann, Max Slevogt, and Emil Nolde acquired a
garden of their own. These gardens provided with a place to linger and offered the painter an
appropriate range of subjects he might study under the most varied light and weather conditions.
The phenomenon of the painter’s garden stems from this period. The play of colours itself was easily
as important as observing the light and the effect of the atmosphere on the colours.
Diversions The variety of establishments found in cities offered numerous options for socializing. Beginning in the 1850s, song and dance interludes offered by restaurants and known as ‘café-concerts’ were especially popular. Such venues supplied the stage for the female clown Cha-U-Kao to perform, for the chanson singer Emélie Bécat to sing risqué songs, and for can-can dancers to flounce their skirts. Vaudeville theatres such as the Moulin Rouge or the dance hall at the Moulin de la Galette in the Montmartre district of Paris also proved attractive. Ballets, operas and operettas, cabarets, theatres, fairgrounds, and circuses were part of a firmly established entertainment industry. Conversations over drinks in smoky pubs and restaurants led to fleeting sexual encounters – and lively artistic exchanges. Ludwig Meidner describes the coffeehouse as a preferred location for meetings, diversions, and pleasures. Yet an oppressive undercurrent often permeated this tremendous bustle, which many painters found particularly striking and worthy of representation. In 1863, Charles Baudelaire described the artist Constantin Guys, the dégagé flâneur of nighttime Paris, as a ‘painter of modern life’. Kirchner and Nolde recorded their experiences exploring Berlin’s nightlife for inspiration in very similar terms.
Diversions. Cafés, Dancers, and Cabaret Life
|
Edgar Degas
Tänzerinnen im Probensaal (Danseuses au foyer), 1895/96 Dancers at Rehearsal, 1895/96 Öl auf Leinwand, 70,5 x 100,5 cm Wuppertal, Von der Heydt-Museum |
|
Ernst Ludwig Kirchner
Zwei Tänzerinnen, 1910/11 Two Dancers, 1910/11 Öl auf Leinwand, 64,8 x 59,6 cm Kochel am See, Franz Marc Museum, Dauerleihgabe aus Privatbesitz |
|
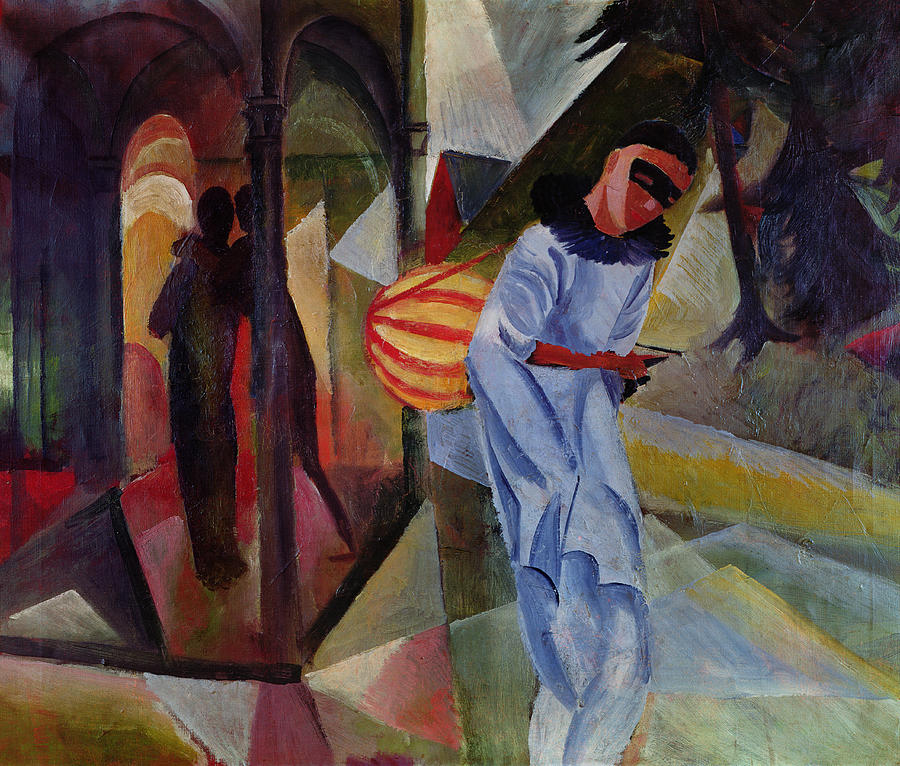
August Macke
Pierrot, 1913 Pierrot, 1913 Öl auf Leinwand, 75 x 90 cm Kunsthalle Bielefeld |
|
Karl Schmidt-Rottluff
Weinstube, 1913 Wine Bar, 1913 Öl auf Leinwand, 76 x 84 cm Berlin, Brücke-Museum |
|
Couples and Relationships
The traditional roles of men and women shifted alongside the social and economic changes of the
nineteenth century. This period gave rise to the concept of the distinct individual. Popular magazines
and novels were filled with such themes as marriages of convenience or love, romantic affairs, and
personal tragedies. Writers created striking psychological portraits of failed marriages: the era of
Emma Bovary, Anna Karenina, and Hedda Gabler commenced in the 1850s.
French and German Impressionism and early Expressionism originated from similar social conditions. Both movements produced a surprising number of pictures of couples and families, many of which were remarkably large in size. In a deliberate rejection of a Biedermeier-era family idyll, these paintings do not simply reflect reality, but rather show new models for familial roles. They emphasize the specific character of the individual rather than a couple’s togetherness or a family’s sense of belonging. Those painted are often turning or looking in different directions. Manet’s work, for example, is characterized by the vacant gaze of some of his subjects. Thus, in various ways, these pictures reflect the shifting gender dynamic of the late nineteenth century.
French and German Impressionism and early Expressionism originated from similar social conditions. Both movements produced a surprising number of pictures of couples and families, many of which were remarkably large in size. In a deliberate rejection of a Biedermeier-era family idyll, these paintings do not simply reflect reality, but rather show new models for familial roles. They emphasize the specific character of the individual rather than a couple’s togetherness or a family’s sense of belonging. Those painted are often turning or looking in different directions. Manet’s work, for example, is characterized by the vacant gaze of some of his subjects. Thus, in various ways, these pictures reflect the shifting gender dynamic of the late nineteenth century.
Artists
Impressionists and Expressionists alike painted themselves in numerous pair and family portraits. Similarly, the standalone artist self-portrait is a recording of a particular moment. It simultaneously expresses an idealized role and functions as an autobiographical statement. Max Slevogt shows himself as a youthful artist, unconventional and approachable. Lovis Corinth stares critically at his mirror image – he finds himself at a crossroads in his life. Max Liebermann, in contrast, consistently represents himself as self-confident. Here, he depicts himself standing in front of his own paintings, wearing a white painter’s apron over a suit. In his self-portrait, Expressionist Karl Schmidt-Rottluff set himself apart from the ‘superficial’ paintwork of the Impressionists. A monocle glints in one eye, while his other eye is closed. And Ludwig Meidner, who belonged to the group known as the ‘Pathetiker’, looks alert and piercing in his self-portrait.
Impressionists and Expressionists alike painted themselves in numerous pair and family portraits. Similarly, the standalone artist self-portrait is a recording of a particular moment. It simultaneously expresses an idealized role and functions as an autobiographical statement. Max Slevogt shows himself as a youthful artist, unconventional and approachable. Lovis Corinth stares critically at his mirror image – he finds himself at a crossroads in his life. Max Liebermann, in contrast, consistently represents himself as self-confident. Here, he depicts himself standing in front of his own paintings, wearing a white painter’s apron over a suit. In his self-portrait, Expressionist Karl Schmidt-Rottluff set himself apart from the ‘superficial’ paintwork of the Impressionists. A monocle glints in one eye, while his other eye is closed. And Ludwig Meidner, who belonged to the group known as the ‘Pathetiker’, looks alert and piercing in his self-portrait.
Portraits of fellow painter friends are less likely to contain this element of scrutiny. Corinth painted
Berlin Secession founder Walter Leistikow as the epitome of the ‘en plein air’ painter. August Macke
portrayed his friend Franz Marc as a discriminating interpreter of the world, with great empathy for
animals and his fellow man.
Art Mediators. Dandies, Connoisseurs, Patrons, and Collectors
Paul and Bruno Cassirer, Julius Meier-Graefe, Hermann Bahr, Herwarth Walden, Rosa Schapire, and
many other art lovers promoted new trends outside the official academic art market in Wilhelmine
Germany.
Collectors and dealers, curators and critics made a strong case for Impressionism and Expressionism. Hugo von Tschudi, then the director of the Nationalgalerie, was important for both art movements. He was the first to buy paintings by French Impressionists for a German museum. And, around the same time, the almanac Der Blaue Reiter, edited by the Expressionists Wassily Kandinsky and Franz Marc, was dedicated to him.
Critics and theorists engaged with both Impressionism and Expressionism, reaching a wide audience through their books, catalogues, articles, and reviews. Many of these art mediators cultivated friendly relationships with the artists they supported, collecting their work and commissioning portraits. The artists’ vivid portraits depict these proponents of Impressionism and Expressionism oscillating between two quite different roles, namely, as the cosmopolitan dandy and the visionary prophet. The portraits record these critics and theorists as intellectual partners on a shared path towards innovation.
Collectors and dealers, curators and critics made a strong case for Impressionism and Expressionism. Hugo von Tschudi, then the director of the Nationalgalerie, was important for both art movements. He was the first to buy paintings by French Impressionists for a German museum. And, around the same time, the almanac Der Blaue Reiter, edited by the Expressionists Wassily Kandinsky and Franz Marc, was dedicated to him.
Critics and theorists engaged with both Impressionism and Expressionism, reaching a wide audience through their books, catalogues, articles, and reviews. Many of these art mediators cultivated friendly relationships with the artists they supported, collecting their work and commissioning portraits. The artists’ vivid portraits depict these proponents of Impressionism and Expressionism oscillating between two quite different roles, namely, as the cosmopolitan dandy and the visionary prophet. The portraits record these critics and theorists as intellectual partners on a shared path towards innovation.
Edvard Munch
Harry Graf Kessler, 1906 Harry Graf Kessler, 1906 Öl auf Leinwand, 200 x 84 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie, erworben durch das Land Berlin |
|
Still Lifes
In 1900, it was a firm principle of modern aesthetics that ‘a beet painted well is better than a poorly
painted Madonna’, to quote Max Liebermann. The hierarchy of genres was no longer irrefutable – the
subject of a painting had become secondary. ‘A bunch of asparagus, a bouquet of roses – these
sufficed for a masterpiece’.
Thanks to Gustave Courbet and the Leibl school in Munich, the still life took on a new significance: It became a place for artistic experimentation. In still lifes, artists addressed painterly questions of composition, colour, and technique. Perspective, light, surfaces, contrasts of colour and shape could be varied and methodically studied even more easily in the controlled environment of the studio than when painting en plein air or when working with a live model. Artists selected familiar items such as apples, flowers, masks, or earthenware based on their forms and colours and positioned these objects in distinctive arrangements.
The subject itself was less important than the act of painting; the still life became the ‘touchstone’ of the artist (Edouard Manet).
Impressionism and Expressionism shared this idea, although each movement adapted the still life to its respective style. The Impressionists’ guiding light was Manet, while for the Expressionists it was Paul Cézanne, whom Julius Meier-Graefe dubbed the ‘father of modernism’.
Thanks to Gustave Courbet and the Leibl school in Munich, the still life took on a new significance: It became a place for artistic experimentation. In still lifes, artists addressed painterly questions of composition, colour, and technique. Perspective, light, surfaces, contrasts of colour and shape could be varied and methodically studied even more easily in the controlled environment of the studio than when painting en plein air or when working with a live model. Artists selected familiar items such as apples, flowers, masks, or earthenware based on their forms and colours and positioned these objects in distinctive arrangements.
The subject itself was less important than the act of painting; the still life became the ‘touchstone’ of the artist (Edouard Manet).
Impressionism and Expressionism shared this idea, although each movement adapted the still life to its respective style. The Impressionists’ guiding light was Manet, while for the Expressionists it was Paul Cézanne, whom Julius Meier-Graefe dubbed the ‘father of modernism’.
Edouard Manet Der Fliederstrauß (Lilas blanc dans un vase de verre), um 1882 Lilacs in a Glass Vase, circa 1882 Öl auf Leinwand, 54 x 42 cm Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie |
|
Behind closed doors
Maurice Maeterlinck’s 1895 play Intérieur instances the importance and relevance of the concept of
the interior, which was experienced and staged as a protected, ‘holy’ alternative to public space. In the
early modern industrial age, interior space was more important than ever before for people’s ideas of
living and selfhood. Women, from whom the emancipation movement was still far off, were intimately
acquainted with the indoor world.
This is why Impressionists and Expressionists alike most often depicted women in their interior
scenes: some preferred women engaging in domestic activities and personal tasks, while others
mainly showed woman as nudes in a studio. Even models whom the painters knew personally
remained largely formal subjects through whom artists might study the relationships between colour
and form or between bodies and space. Renoir painted women, in his own words, as ‘beautiful fruit’,
and as spatial still lifes. Degas and Kirchner sought to arrest movements that were natural and
unfeigned, even commonplace. Fleeting ‘depictions of life’ (Lovis Corinth) were captured in these
pictures, painted as if peeping through a ‘keyhole’ (Edgar Degas). Thus the most intimate (and most
familiar) moments form the alluring, at times voyeuristic, subjects of both Impressionist and
Expressionist interior paintings.
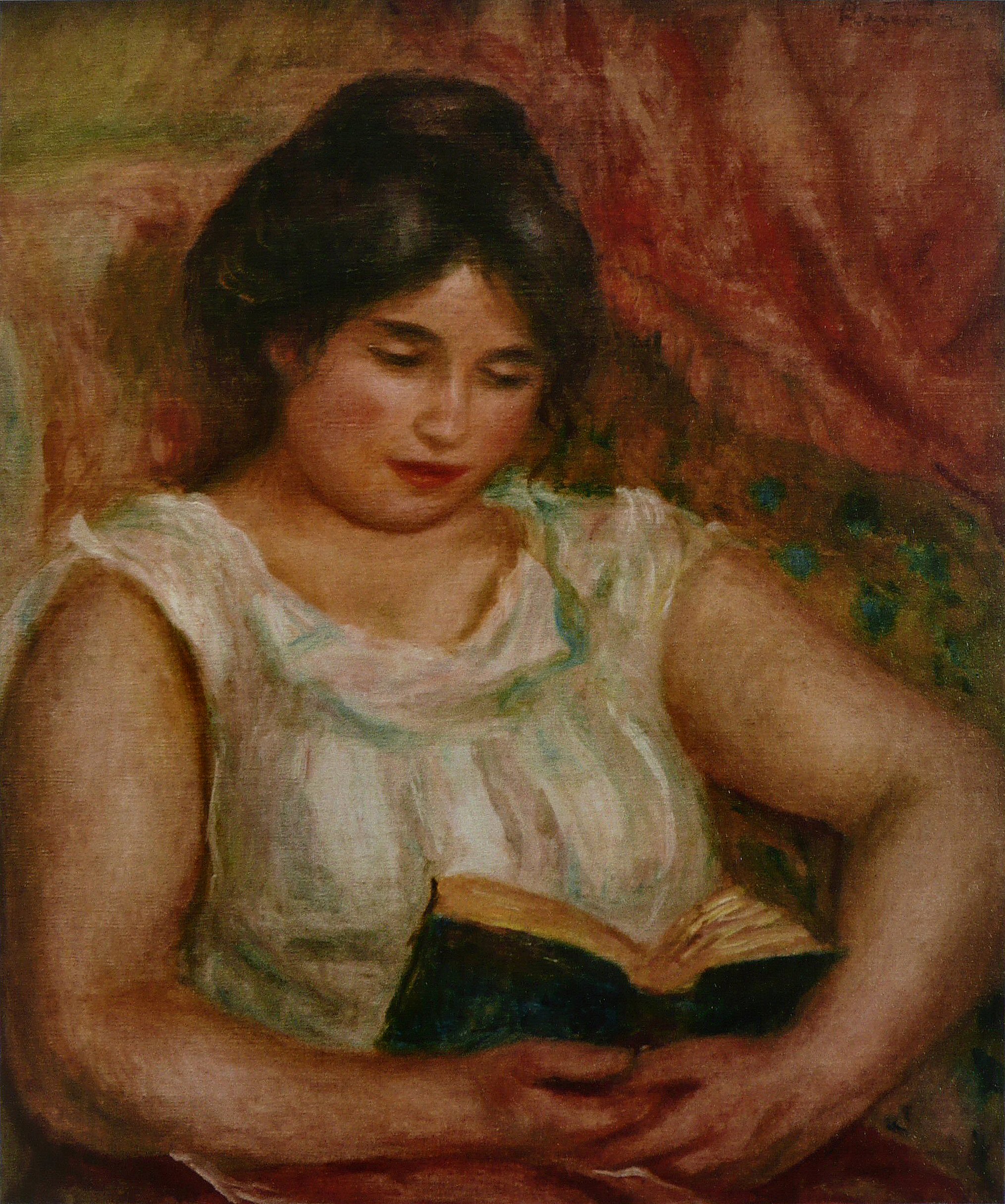
Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Gabrielle bei der Lektüre (Gabrielle lisant), 1906 Gabrielle, Reading, 1906 Öl auf Leinwand, 55 x 46,5 cm Karlsruhe, Staatliche Kunsthalle |
|
Animals
Given the strictures of bourgeois life, the desire to return to nature as a site of origin factors into the many representations of animals in Impressionism and Expressionism. The naturalness of these creatures appealed to artists. The animal was an unencumbered subject with no associated greater significance and it served as a proving ground for a new definition of art. ‘Intangible ideas express themselves in tangible forms,’ wrote August Macke, ‘made tangible through our senses as a star, as thunder, as a flower’ – or, one might add, as an animal.
German Impressionists discovered animals wherever they looked – in the countryside, on the racecourse, in the zoo, and in cages – and were inspired by a hitherto underappreciated wealth of colours, shapes, and movements. These artists merged representations of animals with their environments.
For Franz Marc, the animal was a being with a soul and even became a more general symbol of life. He wanted to paint ‘the animal’s own sense of experience’. From 1913, animals became a means for Marc, Nolde, and Dix to express diffuse yet tangible fears. Curt Herrmann, for example, painted a flamingo, which had recently died in a zoo, as an allegory for the war in 1917.
Given the strictures of bourgeois life, the desire to return to nature as a site of origin factors into the many representations of animals in Impressionism and Expressionism. The naturalness of these creatures appealed to artists. The animal was an unencumbered subject with no associated greater significance and it served as a proving ground for a new definition of art. ‘Intangible ideas express themselves in tangible forms,’ wrote August Macke, ‘made tangible through our senses as a star, as thunder, as a flower’ – or, one might add, as an animal.
German Impressionists discovered animals wherever they looked – in the countryside, on the racecourse, in the zoo, and in cages – and were inspired by a hitherto underappreciated wealth of colours, shapes, and movements. These artists merged representations of animals with their environments.
For Franz Marc, the animal was a being with a soul and even became a more general symbol of life. He wanted to paint ‘the animal’s own sense of experience’. From 1913, animals became a means for Marc, Nolde, and Dix to express diffuse yet tangible fears. Curt Herrmann, for example, painted a flamingo, which had recently died in a zoo, as an allegory for the war in 1917.
Franz Marc Kühe, gelb-rot-grün, 1912 Cows, Yellow/Red/Green, 1912 Öl auf Leinwand, 62 x 87,5 cm Städtische Galerie im Lenbachhaus und Kunstbau, München |
|
Premonitions of War. 1913
Even in the years before the First World War, Wilhelmine empire society was deeply divided, split between bureaucrats, nationalists, and social revolutionaries. Friedrich Nietzsche had critiqued the decline of European culture and morality, questioning his contemporaries’ belief in progress. Anthroposophy, mysticism, socialism, and depth psychology supplied alternative models for explaining society. A series of disasters – including the earthquake in Messina in 1908, the appearance of Halley’s comet in 1910, and the sinking of the Titanic in 1912 – made an apocalypse feel threateningly close at hand. The second Moroccan crisis in 1911 and the Balkan Wars in 1912/13 fuelled this simmering feeling of unease. This powerless sense that the ‘end of days’ (Georg Heym) had arrived was in constant conflict with a societal desire for revolution and renewal. The avant-garde flourished in this atmosphere. The ‘Neue Club‘ was founded in Berlin in 1909. At the club’s ‘Neopathetic Cabaret’, controversial author Frank Wedekind gave readings, as did Heinrich Mann and Franz Kafka, and Arnold Schönberg’s piano pieces were performed there as well. Georg Heym and Jakob van Hoddis forged their ominous visions into powerful figurative verse. And Expressionist painters created lasting images of the era’s lurking sense of uncertainty. |
|
Otto Dix Sonnenaufgang, 1913 Sunrise, 1913 Öl auf Pappe, 50,5 x 66 cm Städtische Galerie Dresden – Kunstsammlung, Museen der Stadt Dresden, erworben mit Unterstützung der Ernst von Siemens Kunststiftung, der Kulturstiftung der Länder, der Hermann Reemtsma Stiftung und der Rudolf-August Oetker Stiftung, 2012 |
|
Jakob Steinhardt Die Stadt, 1913 The City, 1913 Öl auf Leinwand, 61 x 40 cm Staatlichen Museen zu Berlin, Nationalgalerie From the NY Times:
|



















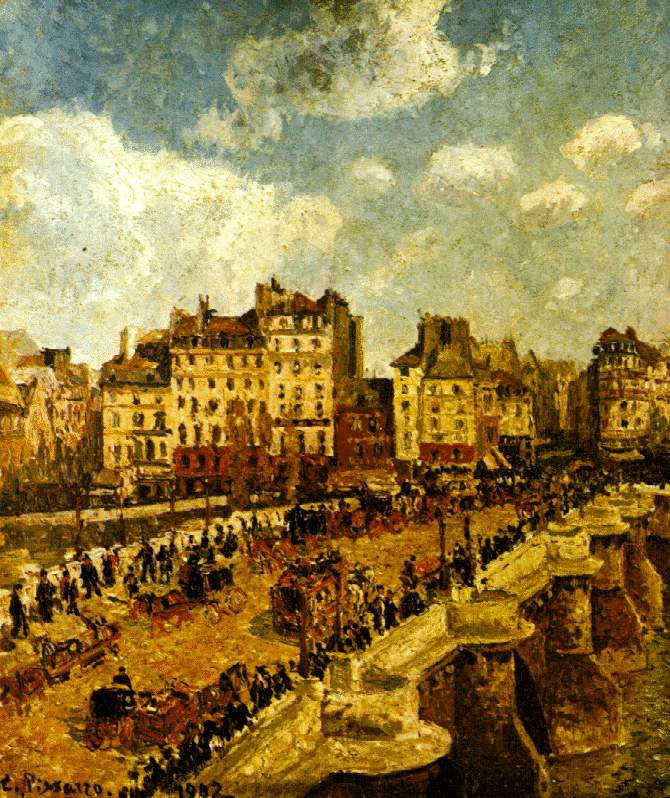








































,_1913.jpg)

